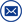
Sf6 gas analyzer structure
Release Time : 2018-02-08 View Count : 次The structural principle of the sf6 gas analyzer. The SF6 gas density meter shown in the above figure is mainly composed of elastic metal curved pipe 1, gear mechanism and pointer 2, double metal strip 3 and other components. In fact, double-layer metal is added to the spring tube type pressure gauge mechanism. Made up of belts. The hollow elastic metal curved pipe 1 is connected to the circuit breaker, and the inner space thereof communicates with the SF6 gas in the circuit breaker, and the end of the elastic metal curved pipe 1 is hingedly connected with the temperature-compensating bimetal strip 3, and the double metal strip 3It is hingedly connected to the gear mechanism and the pointer mechanism 2.

During the process of charging the circuit breaker with sf6 gas analyzer, as the gas pressure gradually increases, the end of the elastic metal curved pipe 1 is displaced in the direction of 4, and the double-layer metal strip 3 is always compensated at 20 °C, also The displacement in the direction of 4 causes the gear mechanism and the pointer 2 to move in the direction in which the density or the pressure indication value increases, and the indication value becomes large. The indication value of the density meter or pressure gauge is not only related to pressure, but also to temperature. In the process of charging SF6 gas to the circuit breaker, due to the sudden expansion and depressurization of SF6 gas, the temperature generally falls below 0 °C from the ambient temperature, and the double metal strip 3 is always compensated at 20。C, but the actual temperature of the SF6 gas cannot be used. The temperature difference between the ambient temperatures is compensated. Therefore, in this case, the indicated value of the density meter does not represent the density or pressure value at the actual temperature of the SF6 gas, nor does it represent the density or pressure value at the ambient temperature. It does not represent the density or pressure at 20 °C.